Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Block Diagram: Controlling a Robotic Arm with VHDL and VLSI
Team: Kimberly Hayes and Daniel Sierra
Faculty Advisor: Dr. Vinod Prasad
Introduction
The Rhino Robotic XR-2 Arm is a mechanical robot arm with six individual servo motors. Each motor controls a different movement of the arm. The arm is controlled by either moving the Wingman joystick or pressing one of the buttons located on the joystick. The Altera Board with verilog hardware description languange (VHDL) code will be used to interface the joystick commands to the robotic arm. See the system block diagram below in Figure 1.
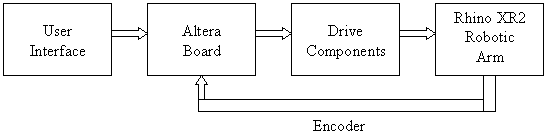
Figure 1: Overall System Block Diagram
User Interface
The user will have two ways in which to control the movement of the arm. The main method of control is the movement of the joystick. Moving the joystick across the x or y-axis would activate a certain sequence of motors to move the robot arm. The second method of control would use the buttons to execute a predefined routine such as returning to a set position or performing a task.
Altera Board
The Altera UP2 Board with a field programmable gate array (FPGA) will be used. A programmed FPGA will contain the VHDL code which will correlate the inputs to the robotic arm movement. The inputs will not just include the user interface, but also the rotary encoder information from each motor. The user interface will be the desired movement and the encoder information, which is in Gray code, will tell what position the motor is in. The code will then need to determine how much the motor will need to move and control it with a pulse width modulated signal. Once the code is completed it will then be turned into gates that will be implemented in very large scale integration (VLSI). The top level software flowchart is shown in Figure 2 below.
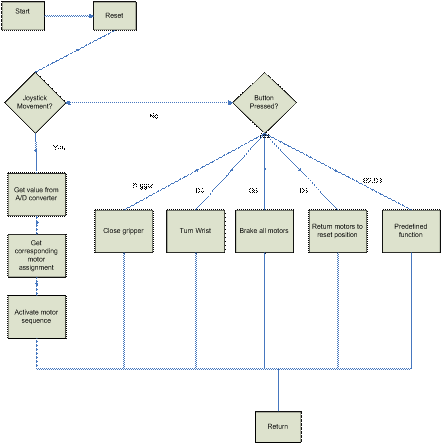
Figure 2: Top level software flowchart
Drive Components
The motors are driven with voltage ranges of +/-12 and +/-24 volts. Since the Altera Board outputs voltages of 0 to 5 volts drive components will need to change the voltage levels. The drive circuitry will also control the direction of the motor. All of this external circuitry will be built with external hardware.
Robotic Arm
The Rhino Robotic XR-2 Arm will be the controlled arm. As stated
before, there are six servo motors that control the movement of the arm. Figure
3 shows the different motors and where each joint is located. See Table 1 for
the designated letter assignment and the position. 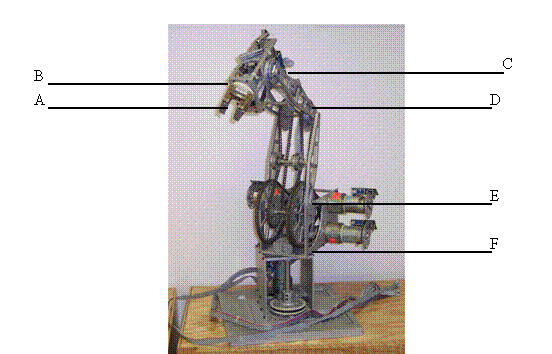
Figure 3: Rhino XR-2 Robotic Arm with Joint Names
|
Motor Letter |
Motor Joint |
|
Motor A |
Grip Close |
|
Motor B |
Grip Turn |
|
Motor C |
Wrist |
|
Motor D |
Elbow |
|
Motor E |
Shoulder |
|
Motor F |
Waist |
Table 1: Motor name and position assignments
Each motor will have its own control signal. This signal is provided from the FPGA through the drive components. With each movement the motor makes, a rotary encoder reads the position off of a disk attached to the motor. This position information is sent back to the FPGA so it knows how much farther the motor needs to be turned or if the motor has turned too far.